
Connecting Deliberative Process Datasets and Ontologies for Enhanced Analysis and Understanding
Connecting Deliberative Process Datasets and Ontologies for Enhanced Analysis and Understanding
The Deliberation Knowledge Graph project aims to connect various deliberative process datasets and ontologies into a comprehensive knowledge graph. This project provides a unified framework for analyzing deliberative processes across different platforms and contexts, from formal parliamentary debates to citizen participation initiatives.
By integrating diverse datasets and ontologies, the Deliberation Knowledge Graph enables researchers, policymakers, and citizens to explore the connections between different deliberative processes, identify patterns, and gain insights into how deliberation works across various contexts.
The project integrates several datasets related to deliberative processes from various sources:
The European Parliament Debates dataset contains structured representations of plenary session debates, converted from verbatim HTML reports into both JSON and RDF formats aligned with the Deliberation Ontology.
This dataset captures the rich deliberative processes of the European Parliament, including speeches, topics, participants, and their political affiliations.
{
"@type": "deliberation:DeliberationProcess",
"deliberation:identifier": "ep_debate_YYYYMMDD",
"deliberation:name": "European Parliament Debate",
"deliberation:hasTopic": [...],
"deliberation:hasParticipant": [...],
"deliberation:hasContribution": [...]
}
Citizen proposals and comments from Madrid's participatory democracy platform, enabling citizens to propose, debate, and vote on city initiatives.
A dataset for deliberation in multi-party problem solving, containing structured conversations aimed at reaching consensus on complex issues.
Feedback and initiatives from the European Commission's public consultation platform, where citizens and stakeholders can provide input on EU policies.
Data from a deliberative democracy experiment inspired by Jürgen Habermas's theories of communicative rationality and deliberative democracy.
Data from Barcelona's implementation of the Decidim participatory democracy platform, showcasing citizen engagement in urban planning and policy development.
Transcripts of oral arguments before the United States Supreme Court (2017-2021), providing insights into legal deliberation at the highest judicial level.
The core ontology of this project, which integrates concepts from the ontologies listed below:
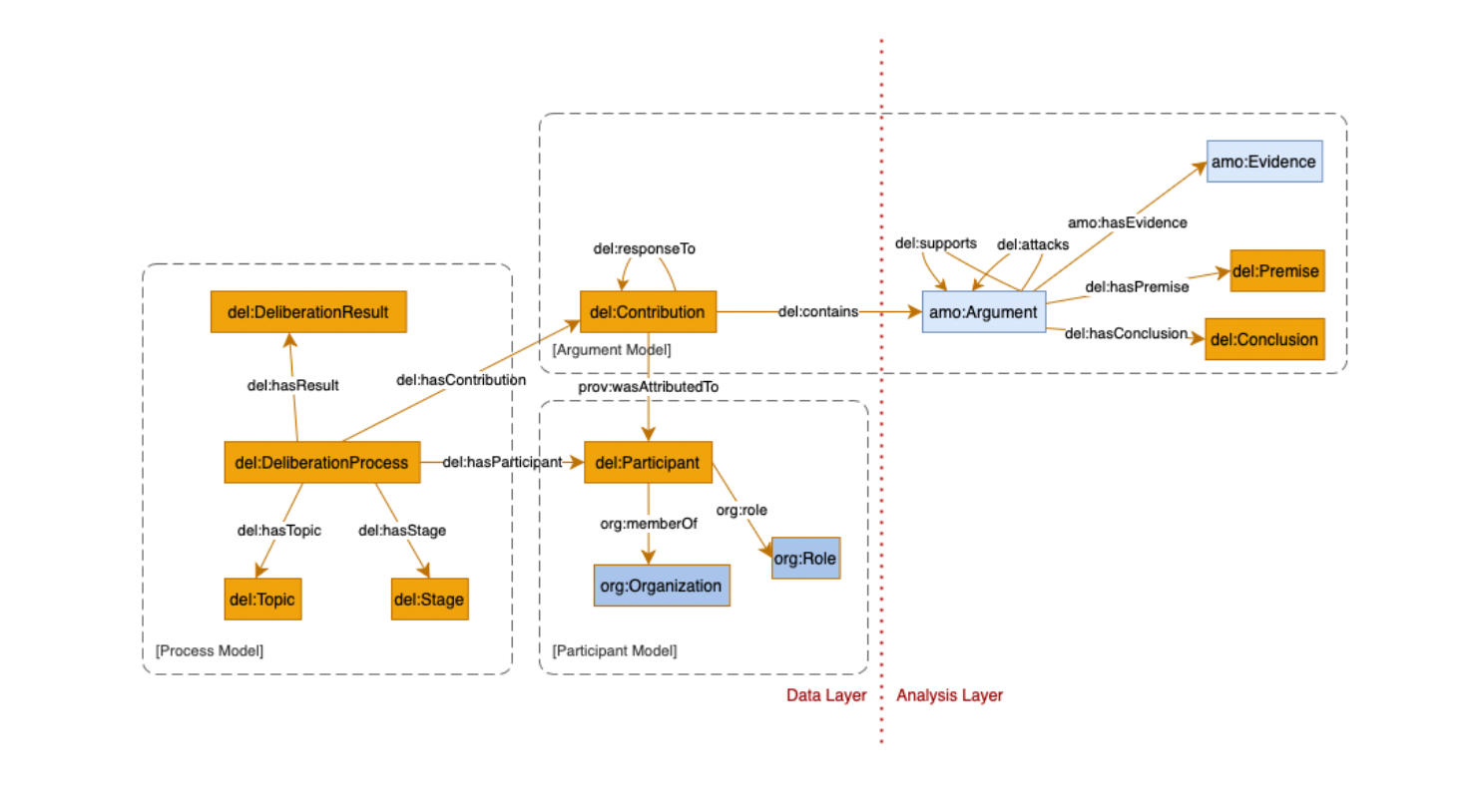
The mappings.owl file contains explicit mappings between the Deliberation Ontology and other standard ontologies like FOAF, Dublin Core, SIOC, AIF, and LKIF. These mappings enable interoperability and integration with existing semantic web resources.
Key mapping relationships include:
| Ontology | Available (rdf | xml | doc) | Name | Description | Language | Jurisdiction/Scope | Reference / Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DELIB | rdf | doc | DELIB Ontology | Geared to capture essential elements of deliberative processes and participant interactions, emphasizing how contributions, interventions, and outcomes connect within a deliberation. | en | all |
OWL) Documentation |
| AIF | rdf | doc | Argument Interchange Format | A core ontology designed to represent and exchange argument structures, enabling interoperability between argumentation tools. Developed to capture premises, conclusions, and relations in structured debate. | en | all |
AIF (OWL) Documentation |
| SIOC | rdf | doc | SIOC Ontology | The Semantically-Interlinked Online Communities (SIOC) Ontology provides concepts for describing online community activities, including posts, forums, and user accounts. Extended with argumentation structures to support semantic linking of discussion threads and arguments. | en | all |
SIOC (RDF) Documentation |
| FOAF | rdf | doc | FOAF Ontology | Friend of a Friend (FOAF) describes persons, their activities, and their relations to other people and objects. Often used to model participant identities, organizations, and groups in social web contexts. | en | all |
FOAF (RDF) Documentation |
| DC | rdf | doc | Dublin Core | A set of vocabulary terms used to describe web resources (title, creator, subject, date, etc.). Widely used for metadata, providing consistent description properties (e.g., dc:title, dc:creator). | en | all |
DC (RDF) Documentation |
| LKIF | rdf | doc | LKIF Ontology | The Legal Knowledge Interchange Format (LKIF) covers concepts for norms, rules, and legal reasoning. Often used to integrate legal arguments with broader domain ontologies in e-government and e-participation. | en | eu |
LKIF (OWL) Documentation |
| IBIS | rdf | doc | Issue-Based Information System | A classic method for modeling and visualizing issues, ideas, and arguments in a structured format. Widely used for deliberative problem-solving and mapping various positions and solutions. | en | all |
IBIS (OWL) Documentation |
| AKN | xml | doc | Akoma Ntoso | A structured XML schema defining representations of parliamentary, legislative, and judiciary documents (also known as LegalDocML). Facilitates interoperability for legal and legislative texts across jurisdictions. | en | all |
Akoma Ntoso (OASIS) Documentation |
| Metalex | xml | doc | Metalex | An open XML interchange format for legal and legislative resources, enabling consistent structuring and referencing of sources of law, often used alongside Akoma Ntoso. | en | eu |
Metalex Homepage CEN Standards |
| LegalRuleML | xml | doc | LegalRuleML | A framework extending RuleML with legal rule modeling capabilities, enabling interoperable exchange of legal arguments, norms, and complex reasoning structures in a machine-readable format. | en | all |
LegalRuleML (OASIS) Documentation |
The Deliberation Knowledge Graph project provides conversion tools to transform various deliberation datasets into RDF format compatible with the deliberation ontology:
| Dataset | Conversion Script | Input Format | Output Format | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU Parliament Debates | data/EU_parliament_debates/convert_json_to_rdf.py |
JSON | RDF/XML | Converts structured JSON representations of EU Parliament debates to RDF format |
| US Supreme Court Arguments | data/US_supreme_court_arguments/convert_to_rdf.py |
CSV | RDF/XML | Converts US Supreme Court oral argument transcripts to RDF format |
| Decide Madrid | data/decide_Madrid/convert_to_rdf.py |
CSV | RDF/XML | Converts Decide Madrid proposals and comments to RDF format |
| DeliData | data/delidata/convert_to_rdf.py |
TSV | RDF/XML | Converts DeliData deliberation conversations to RDF format |
| Habermas Machine | data/habermas_machine/convert_to_rdf.py |
Parquet | RDF/XML | Converts Habermas Machine deliberation experiment data to RDF format |
| EU Have Your Say | data/EU_have_your_say/convert_to_rdf.py |
CSV | RDF/XML | Converts EU Have Your Say feedback and initiatives to RDF format |
| Decidim Barcelona | data/decidim_barcelona/convert_to_rdf.py |
CSV | RDF/XML | Converts Decidim Barcelona proposals, meetings, and comments to RDF format |
All conversion scripts follow a two-step process:
convert_json_to_rdf.py scriptThis approach ensures consistency across all datasets and makes it easy to add new datasets in the future.
Below are separate Mermaid.js graphs showing how each ontology's core classes and properties map to the Deliberation Ontology (Del). We have extracted only the relevant portion of the large integrated diagram, so you can view them in smaller chunks, per ontology.
Each subgraph above focuses on how the Deliberation Ontology Graph maps to or extends the respective ontology's classes and properties. By splitting the overall mapping into smaller diagrams, we ensure that each relationship set is easier to inspect, maintain, and update.
Comprehensive documentation for the Deliberation Knowledge Graph project: